Bitcoin trades 24/7 across thousands of exchanges, leaving a massive digital footprint—from millisecond price ticks to on-chain transaction flows. This data abundance has fueled a natural question:
Can AI models read the future of Bitcoin’s price?
The promise seems intuitive. Machines can sift through terabytes of data, spot patterns humans miss, and execute trades faster than thought. Yet the reality is more nuanced. AI models can be powerful tools for understanding Bitcoin’s behavior, but they are far from crystal balls.
This article breaks down how the leading AI approaches actually work, where they excel, where they struggle, and how professional traders really use them in practice.
The Promise (and Myth) of AI Bitcoin Price Prediction
Why AI Feels Right for Crypto
Bitcoin’s price is notoriously volatile—it can swing 10% in an hour based on a tweet, a regulatory news flash, or liquidation cascades in derivatives markets. However, volatility does not mean randomness.
Bitcoin’s price is shaped by measurable signals:
- Past price momentum
- Trading volume and liquidity
- On-chain activity (who is moving coins and when)
- Market sentiment (social media, news tone)
- Macro trends (Fed policy, liquidity cycles)
These are the exact types of patterns machine learning was designed to capture. Unlike traditional financial markets that operate 9am–5pm with limited data sources, crypto markets run nonstop and generate real-time signals from dozens of layers—price, derivatives, wallets, social networks, news feeds. This richness is AI’s playground — and it’s also why more and more traders are experimenting with AI-driven systems, similar to the workflows we cover in our AI tools for crypto traders guides on aicryptobrief.com.
Forecasting ≠ Fortune Telling
Here’s the critical distinction: forecasting is probabilistic—estimating the likelihood of price movements within a band, given current conditions. Fortune telling is claiming certainty about the future.
Serious AI models in crypto operate as forecasters. They might output something like:
“Bitcoin has a 65% probability of staying between $96k and $102k in the next 7 days, given current orderbook pressure and funding rates.”
That is useful information for risk management. It is not a guaranteed trade signal. The market remains uncertain, novel events occur, and models can be wrong.
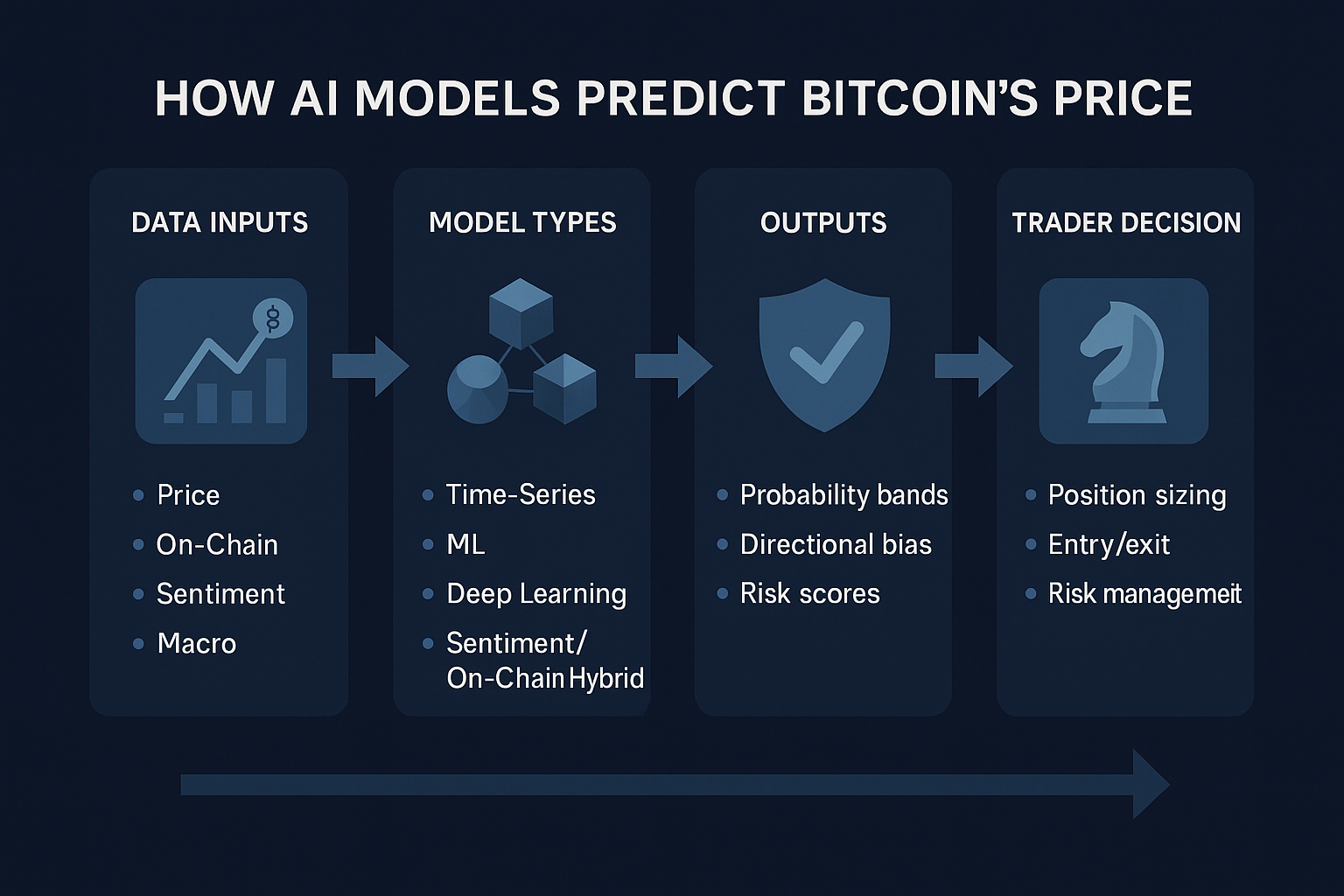
Data: What AI Models Actually Look At
Before diving into model architectures, it helps to understand the data layer. A model is only as good as its inputs. Crypto offers a feast of data types:
Market Data
- OHLCV (Open, High, Low, Close, Volume) at various timeframes (1-minute to daily)
- Orderbook snapshots (bid/ask levels, depths, pressure)
- Liquidation volumes, mark prices, funding rates on derivatives exchanges
On-Chain Metrics
- Addresses and transaction flows (e.g., coins moving from exchanges to cold storage = potential HODLing)
- Realized value, entity-adjusted metrics, whale movement thresholds
- Mining activity, miner revenue, difficulty adjustments
Sentiment & News
- Tweet volume and sentiment polarity from X (formerly Twitter)
- News headline sentiment (positive/negative bias)
- Google Trends search volume for “Bitcoin”
- Social media comment tone and urgency signals
Macro & External
- US dollar index and Federal Reserve rate expectations
- Equity market correlation (S&P 500, tech stocks, gold)
- Volatility indices (VIX)
Key insight: Data quality often matters more than model sophistication.
A simple model trained on clean, well-sourced data often beats a fancy deep learning model trained on garbage inputs. “Garbage in, garbage out” is as true in AI as anywhere.
Main Types of AI Models Used for Bitcoin Forecasting
1. Traditional Quant & Time-Series Models
How They Work
Traditional statistical models like ARIMA (AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average) and GARCH (Generalized Autoregressive Conditional Heteroskedasticity) assume price movements follow predictable patterns based on their own history.
- ARIMA learns the mathematical relationship between past prices and future prices.
- GARCH specifically models volatility clustering—the tendency for quiet periods and volatile periods to cluster together.
Data Input
- Mainly historical price data (daily or intraday)
- Sometimes augmented with volatility measures or macro indicators
Strengths
- Transparent and interpretable—traders understand why the model made a forecast
- Computationally light and fast to train
- Good for capturing short-term mean reversion (prices tend to bounce after extreme moves)
- EGARCH variants capture asymmetry (negative shocks hit volatility harder than positive ones)
Weaknesses
- Assume stationarity or linear relationships; Bitcoin price is highly non-linear
- Smooth out sudden jumps and black swan events (regulatory bans, exchange hacks)
- Limited to price history; they ignore sentiment, macro, on-chain data
- Backtests may show 5–10% forecasting error on short-term price, but live performance often disappoints
Typical Use
- Baseline benchmarks for volatility forecasting
- Short-term tactical signals (1–7 days)
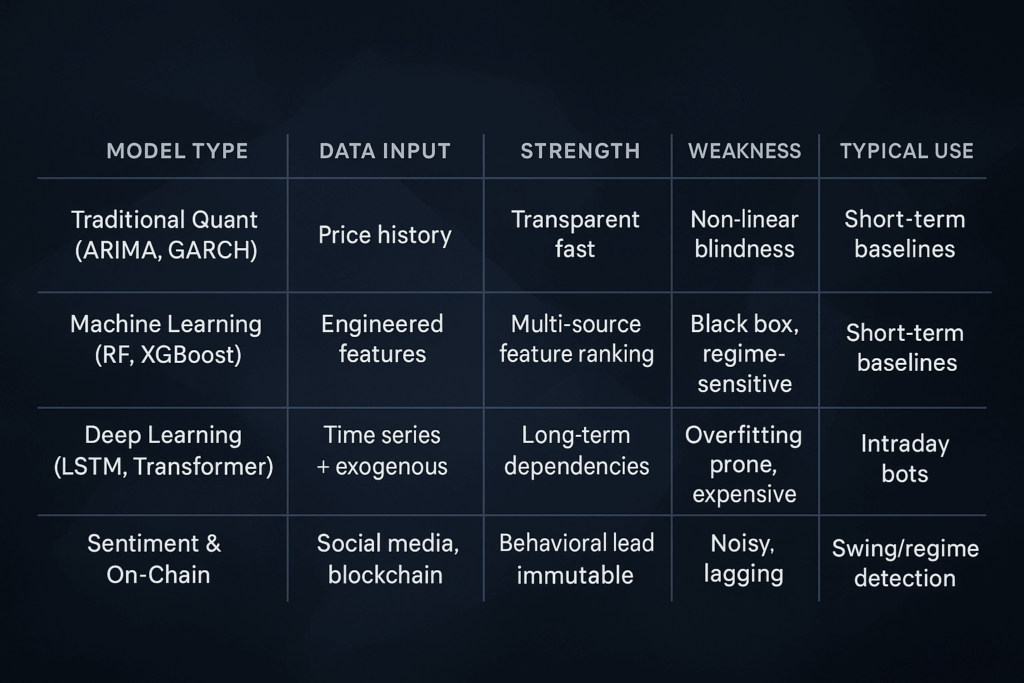
2. Machine Learning Models
How They Work
Machine-learning models like Random Forest and XGBoost (Extreme Gradient Boosting) treat Bitcoin price prediction as a classification or regression task. They learn which combinations of features—e.g., volume spike + high funding rate + positive sentiment—correlate with price rises.
Unlike ARIMA, they don’t assume any fixed mathematical form; they find patterns by:
- Building decision trees (Random Forest)
- Boosting weak learners into a strong ensemble (XGBoost)
Data Input
Engineered features such as:
- Moving averages, RSI, MACD
- Volume ratios and orderbook imbalance
- On-chain metrics and whale flows
- Sentiment scores, funding rates, open interest
- Sometimes hundreds of features
Strengths
- Handle non-linear relationships well
- Naturally incorporate multiple data types (price + on-chain + sentiment)
- Can rank which features matter most (e.g., funding rates > social media volume)
- Robust to overfitting if hyperparameters are tuned carefully
Weaknesses
- “Black box” nature—hard to explain why a specific trade signal was generated
- Require significant feature engineering and domain expertise
- Prone to overfitting if trained only on in-sample data
- Performance drops sharply when market regimes shift (bull → bear, crisis periods)
- Backtest accuracy does not translate 1:1 to live trading (costs, slippage, latency)
Typical Use
- Mid-term signals (1–30 days)
- Ranking coins or setups by probability
- Combining with traditional technical analysis
3. Deep Learning Models
How They Work
Deep learning, especially Recurrent Neural Networks (LSTM, GRU) and Transformer architectures, is designed to learn temporal patterns.
- LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) has “memory cells” that decide what to remember from far-back price history and what to forget from recent noise.
- Transformers use an attention mechanism to focus on the most relevant parts of the historical sequence, even if they occurred far in the past.
A typical workflow: feed 60 days of hourly price data + volume into an LSTM layer. The model learns patterns like:
“When volume spiked 3 weeks ago followed by this specific pattern of closes, the next 24 hours tend to move up.”
Transformers add parallel computation and explicit attention weights, making them faster and sometimes more accurate.
Data Input
- Time-series data (price, volume, orderbook state, even raw tick data)
- Optionally exogenous variables (sentiment, macro indicators, funding)
Strengths
- Capture long-term dependencies (patterns from weeks back matter for today)
- Handle high-frequency data, suitable for intraday predictions
- Often outperform ARIMA and basic ML in academic Bitcoin studies
- Attention mechanism provides some interpretability (which past events mattered)
Weaknesses
- Require large amounts of clean training data; overfit easily on small datasets
- Extremely difficult to explain to a non-ML trader or regulator
- Backtested performance on old data (2018–2021 bull run) often fails in new regimes (2022 bear, new narratives, liquidity crunches)
- Computationally expensive; require GPU infrastructure and careful tuning
Typical Use
- Intraday trading bots
- High-frequency signal generation
- Price-band forecasts (likely support/resistance zones)
4. Sentiment & On-Chain AI Models
How They Work
These models blend behavioral and on-chain data to predict price.
A sentiment model might use NLP (Natural Language Processing) to score X/Twitter posts and news as bullish, bearish, or neutral, then combine that with on-chain flow analysis (large addresses buying vs. selling). The hypothesis:
- When retail is euphoric and whales are selling, a top is near.
- When sentiment crashes but whale accumulation rises, a bottom may be forming.
On-chain metrics include:
- Realized cap (value of coins at the price they last moved)
- Coin age (old coins awakening as early indicator)
- Entity flow (tracking addresses linked to exchanges, miners, known funds)
Data Input
- Social media text and news feeds (processed with BERT-style NLP models)
- Blockchain transaction data and entity clustering
- Exchange inflows/outflows
Strengths
- Capture behavioral shifts before they fully reflect in price
- Help identify FOMO peaks and capitulation bottoms
- On-chain metrics are transparent and hard to manipulate
- Hybrid models (on-chain + price + macro) can reach meaningful directional accuracy in research settings
Weaknesses
- Sentiment is noisy; retail often posts bullish comments at tops and bearish comments at bottoms
- On-chain flows can lag—accumulation from two weeks ago may already be priced in
- Social data is biased (X skews toward traders, not long-term holders)
- News sentiment can be gamed; paid FUD and hype distort genuine signal
Typical Use
- Swing-trading signals (3–14 days)
- Identifying trend exhaustion and possible reversals
- Tracking macro narratives and crowd psychology
5. Hybrid & Ensemble Approaches
How They Work
Instead of relying on a single model, many quant funds use hybrid or ensemble systems. For example, a stack might:
- Use an LSTM for price momentum
- Use XGBoost for on-chain anomaly detection
- Use a sentiment classifier for euphoria/despair scores
- Combine outputs via voting or weighted averaging
An ensemble might train multiple architectures (5 LSTM variants, 3 XGBoost models, plus a GARCH volatility model) and aggregate their predictions. If 7 out of 10 models predict “up,” signal strength is higher than if only one model did.
Data Input
- All of the above: price, volume, derivatives, on-chain, sentiment, macro
Strengths
- Exploit strengths of each method; reduce individual model bias
- More robust to regime shifts (different components perform better in different conditions)
- Can provide probabilistic outputs like: “66% chance of +2% move in next 48 hours”
Weaknesses
- Extremely complex; harder to debug when predictions go wrong
- Slower to train and backtest; aggregation logic itself becomes another model
- Overfitting risk multiplies if individual models are already overfit
- Real-world performance still lags backtests significantly
Typical Use
- Institutional risk engines
- Multi-timeframe strategy frameworks
- Quantitative hedge fund models
How Reliable Are These AI Predictions?
Here’s the uncomfortable truth: backtesting results are almost always better than live trading results.
The Backtest-to-Live Gap
A strategy that achieved 70% win rate over 5 years of backtesting often sees 45–50% win rate live. Why?
- Overfitting: Researchers tune model parameters until backtest metrics shine, but the model has memorized the training data rather than learned general patterns. It’s like memorizing answers to last year’s exam and assuming you’ll ace a different exam.
- Non-stationary markets: Bitcoin’s regime shifts. In a 2017 bull run, simple momentum works; in a 2022 crash, completely different factors dominate. A model trained on 2017–2019 data fails when applied to 2022.
- Changing narratives: NFTs boom → DeFi summer → AI tokens → new narratives. Economic conditions shift (0% rates → 5%+ Fed rates). Regulation evolves. None of this is stable.
Hidden Biases in Backtesting
- Survivorship bias: Only looking at Bitcoin’s history ignores the hundreds of failed coins that were hyped and died.
- Look-ahead bias: Using data or events that weren’t known at the time of the trade (for example, future halving impact baked into earlier years).
- Recency bias: Over-optimizing for the most recent move, which is often an outlier.
- Slippage & latency: Backtests assume perfect fills at quoted prices; live trading faces slippage, especially during volatility spikes.
Regime Change & Black Swans
Even a well-built model can fail catastrophically when the market regime shifts. An LSTM trained on 2021 bull-market patterns collapsed in 2022 when macro conditions (rates rising) and on-chain dynamics (whales capitulating) inverted. The model had never seen such a regime; it had no learned response.
Black swan events—the FTX collapse, LUNA implosion, sudden regulatory bans, exchange hacks—are inherently unpredictable. No historical model can forecast what has never happened. These events effectively reset the AI model’s foundation.
The Non-Stationary Problem
Classical time-series models assume the underlying process is stationary (patterns repeat). Bitcoin is decidedly non-stationary: its volatility, correlation with macro assets, and driver dynamics change over time.
Markov-switching and regime-switching models attempt to capture this by identifying discrete market states (bull, bear, high volatility, consolidation), but they often lag reality—the regime is identified after the critical move.
How Traders Actually Use AI Models in Practice
AI as a “Second Opinion,” Not an Oracle
Seasoned traders do not feed AI predictions directly into blind order execution. Instead, they tend to:
- Generate probability bands
- AI model outputs: “Bitcoin likely trades between $95k–$99k over the next 48 hours (70% confidence).”
- Cross-reference with other signals
- The trader overlays this with technical analysis (support/resistance), on-chain data (whale positions), macro calendar (Fed announcements), and risk assessment.
- Decide scenario probabilities
- “50% chance of mean reversion to $97k, 30% chance of breakout to $101k, 20% chance of choppy consolidation.”
- Size positions accordingly
- A $100k portfolio might take a $5k position if conviction is moderate instead of going all-in.
- Use automation for execution
- Once a setup is confirmed, automation handles order placement, position management, and stop losses—removing emotion.
This mindset is very similar to how we recommend using AI in our Weekly Crypto Market Analysis series: AI adds context, not certainty.
Real-World Workflow Example
Day 1 – Morning
- AI ensemble flags: “Funding rates are extremely positive (over-leveraged longs). On-chain shows whale distribution starting. Sentiment remains euphoric. Short-term pullback risk: 60% confidence.”
- Trader checks BTC chart: spots a double-top pattern at $100k.
- Macro context: next Fed meeting in two weeks; funding frothy.
Decision:
“Medium term still bullish, but short-term correction is likely. I’ll go long only if we dip to $97k with a tight stop at $95.5k.”
Day 2 – Afternoon
- Bitcoin pulls back to $97.2k (AI flagged this zone).
- Trader enters a modest long position.
- Sets automated stop loss at $95.5k and target at $101.5k.
Day 4
- Bitcoin recovers to $101.2k.
- Trader exits 60% of the position for a small profit.
- Holds the remaining 40% with a trailing stop in case the trend extends.
In this flow, AI provides probabilistic guidance and regime context, not a magic answer.
Practical Retail-Friendly Tools
Not every trader builds custom models. Retail traders rely on accessible AI-powered tools such as:
- On-chain dashboards (Glassnode, CryptoQuant): pre-built metrics like whale transactions, realized cap, spent output profit/loss.
- AI-assisted TA bots (TradingView scripts, third-party ML engines): scan charts for pattern confluence and alert on extremes.
- Sentiment aggregators (Santiment, LunarCrush): combine social sentiment, whale activity, and price action.
- Backtesting platforms (Backtrader, ccxt, custom Python notebooks): allowing simple ML-based strategies, backtests, and paper trading.
The key: these tools are filters (reducing noise, highlighting high-probability setups) and context providers (showing what regime we’re in), not guaranteed trade generators.
Risks, Biases, and Ethical Concerns
The Herding Problem
When many traders use the same AI model (or highly correlated ones), their buying and selling become synchronized. This creates artificial pressure:
- A widely followed AI forecast saying “buy the dip at $96k” can become self-fulfilling if enough traders act on it—until the crowd exits and the move reverses violently.
If AI-driven trading eventually accounts for most crypto volume, the feedback loops around a single signal could amplify drawdowns during crashes.
Over-Reliance & Signal Overconfidence
Some traders and paid “signal groups” aggressively hype AI predictions:
“My model is 90% accurate!”
Often, that claim is based on cherry-picked backtests. Retail followers pay for signals, only to suffer heavy drawdowns when the model hits a regime shift or a black swan event.
Ethically, selling AI forecasts as guaranteed trades is fraud, yet it happens frequently in the crypto space.
Transparency & Explainability
Deep learning models are largely black boxes. A trader doesn’t really know why the transformer decided to short Bitcoin at $98k—only that it produced a “short” signal.
In regulated markets (stocks, forex), explainability is increasingly required. Crypto is less regulated for now, but as institutions enter, demand for Explainable AI (XAI) techniques (SHAP, LIME, attention visualizations) will grow.
Model Drift & Adaptation Lag
Markets evolve; models do not magically update overnight.
- A model trained in 2023 implicitly assumes 2023 macro conditions.
- When the Fed pivots, liquidity shifts, or a new structural narrative appears in 2024–2025, those assumptions break.
Retraining takes time. Meanwhile, live traders are already adapting, often using on-chain flows and discretionary context faster than the AI can re-learn.
Conclusion
AI is a powerful analytical tool, not a fortune-telling device. Top AI models—LSTM networks, ensemble ML systems, transformer architectures, sentiment + on-chain hybrids—can parse vast data streams and surface high-probability scenarios. They excel at:
- Identifying regimes (bull vs. bear, trending vs. ranging)
- Ranking signals (which indicators matter most right now)
- Reducing noise and filtering out many false breakouts
- Automating execution and monitoring without emotion
However, they struggle with:
- Black swan events and sudden regime changes
- Live execution friction (slippage, latency, costs)
- Non-stationary markets that break historical patterns
- Overfitting and poor generalization to unseen data
If you choose to use AI models in your own trading:
- Treat AI outputs as probabilistic guidance, not certainty.
- Combine AI signals with macro analysis, on-chain flows, and technical setups.
- Size positions conservatively; never go all-in on an AI prediction.
- Backtest with realistic assumptions (fees, slippage, out-of-sample data).
- Monitor model performance regularly; be willing to retire a model if live results diverge from backtests.
- Diversify: use multiple models and signal types; avoid concentration in one “magic” system.
Bitcoin will remain volatile and partially unpredictable. AI can make you better informed, but not omniscient. The traders who win are those who use AI as a second opinion in a diversified toolkit—combined with disciplined risk management—not as a replacement for it.
Discover more from aiCryptoBrief.Com
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.


