You’ve probably seen the headlines already:
“Our AI crypto bot made 300% APY while you sleep.”
“Plug in this AI strategy and never miss a pump again.”
If you’ve read our “AI Crypto Trading Bots: The Complete 2025 Beginner’s Guide” on aicryptobrief.com, you already know the basics: bots can automate trades, AI can help with signals, and risk management is non-negotiable.
But there’s a deeper question most guides skip:
What actually happens inside an AI crypto trading bot from the moment it sees market data to the moment it sends an order to Binance, Bybit, or a DEX?
This article focuses on that “under the hood” view:
- How AI bots collect and structure data
- How machine learning models generate probabilities and signals
- How those signals become position sizes, entries, exits, and risk limits
- How everything connects to APIs, smart contracts, and real orders
If you want setup steps, types of bots, or safety checklists, use this as a companion to the Day 1 beginner guide. Here, we zoom in on mechanics and architecture so you understand what your “AI bot” is really doing.
⚠️ Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and is not financial advice. Crypto trading and automated strategies involve substantial risk. Always test with small amounts and never trade money you can’t afford to lose.
1. Quick Recap: Where AI Bots Fit in the Trading Stack
Traditional crypto bots = rule engines:
- “If RSI < 30 → buy.”
- “If price touches support → place limit order.”
AI crypto trading bots add a learning component on top:
- Collect far more data than humans can track manually
- Use ML models to estimate probabilities or regimes
- Feed those estimates into rules about when, how much, and how to trade
Most real-world “AI bots” are hybrids:
- AI does signal generation / filtering / regime detection
- Human-defined logic still controls risk caps, position sizing, and execution rules
To understand them properly, you need to follow the data all the way through the pipeline.
2. Data Pipeline: From Market Chaos to Clean Features
Before any prediction, the bot needs to turn noisy, messy crypto data into something a model can understand.
2.1 Core Market & Indicator Data
This is the foundation every bot uses:
- OHLCV candles: open, high, low, close, volume across multiple timeframes
- Indicators derived from OHLCV, for example:
- Moving averages (20/50/200)
- RSI, MACD, Stochastics
- Bollinger Bands
- ATR (volatility)
- Order book imbalance (bid vs ask depth)
The bot typically pulls these through:
- Exchange REST APIs (historical data)
- WebSocket streams (real-time ticks)
Internally, this becomes a time-series feature table:
rows = time steps, columns = features like “RSI_1h”, “MA20_4h / MA50_4h”, “ATR_1d”, etc.
2.2 On-Chain & Derivatives Context
More advanced AI bots go beyond price:
- On-chain metrics like:
- Exchange inflows/outflows (potential sell or accumulation pressure)
- Whale transfers (large wallets moving coins)
- Active addresses and transaction counts
- Stablecoin mint/burn activity
- Derivatives data from futures markets:
- Funding rates (are longs or shorts paying more?)
- Open interest (how much leverage is in the system?)
- Recent liquidations (short/long squeezes)
These often come from analytics APIs or in-house indexers, then get normalized into numeric features:exchange_inflow_24h, whale_netflow, funding_rate_8h, oi_change_1h, etc.
2.3 Sentiment & Meta Signals
This is where AI often shines:
- Social sentiment: volume and tone of mentions on X/Twitter, Reddit, Telegram
- News sentiment: NLP models tagging headlines as bullish/bearish/neutral
- Composite indicators: Fear & Greed style scores, trend momentum scores
- Meta features: time of day, day of week, proximity to major events (CPI, FOMC, ETF decisions)
All of this is turned into numbers:
sentiment_scorebetween −1 and +1fear_greed_indexbetween 0 and 100news_bearish_densityas a 0–1 ratio
The final result: a feature matrix that looks like a giant spreadsheet of numbers. That’s what the AI model actually sees
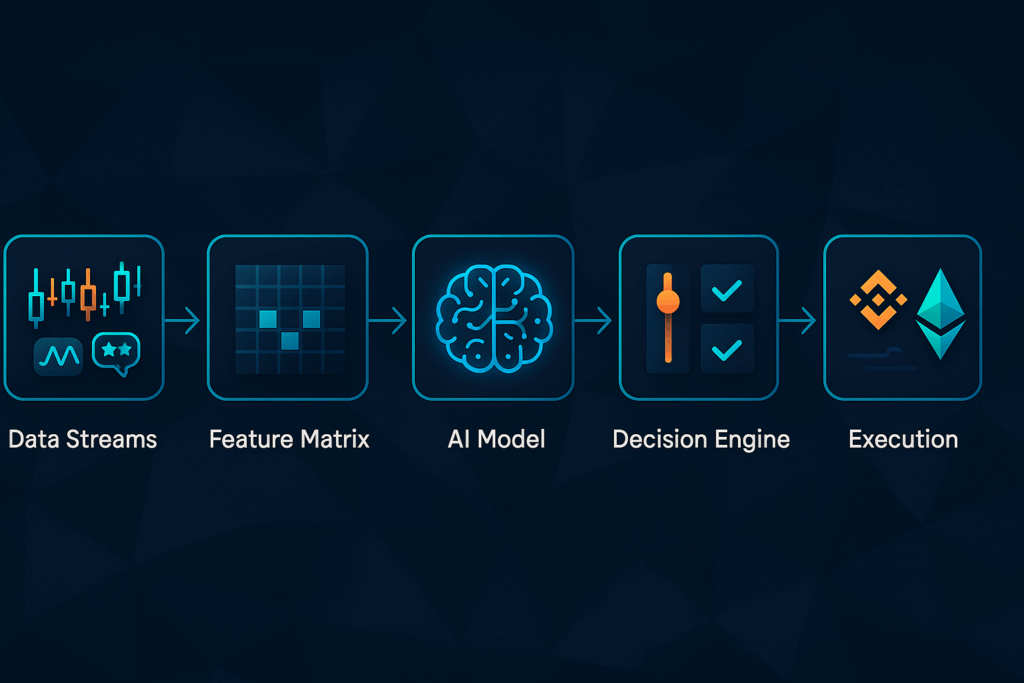
3. The AI Brain: What These Bots Actually Predict
Once the bot has a feature set, the AI model tries to answer well-defined questions. It’s not predicting the future like a crystal ball; it’s doing pattern recognition based on history.
3.1 Common Prediction Tasks
Most AI trading systems focus on one or more of these:
- Direction classification
- “Will price be higher, lower or roughly unchanged in the next X hours?”
- Output example:
- Up: 0.64
- Down: 0.21
- Flat: 0.15
- Return / volatility estimation (regression)
- “What’s the expected % move over the next 4 hours?”
- “How volatile is the next day likely to be?”
- Regime classification
- “Is the market trending up, trending down, or range-bound?”
- “Is this a high-volatility or low-volatility regime?”
Some bots also predict event-like probabilities, such as:
- “Probability of a 5%+ drawdown in the next 24h”
- “Probability of a funding-rate squeeze (excessive longs/shorts)”
3.2 Model Families You’ll See in Practice
Without getting too theoretical, these are the usual engines:
- Tree-based models (Random Forest, XGBoost, LightGBM)
- Great with tabular indicator + on-chain + sentiment features
- Neural networks
- LSTMs / Transformers for time-series and sequential patterns
- Smaller Transformer/NLP models for news & social sentiment
- Ensembles
- Combine several models and only trade when they broadly agree
For you as a trader, what matters is less “which algorithm” and more:
- What is it predicting?
- On what timeframe? (15m, 4h, daily?)
- With what average accuracy / edge after fees and slippage?
If a platform can’t answer those questions clearly, “AI” is probably more marketing than substance.
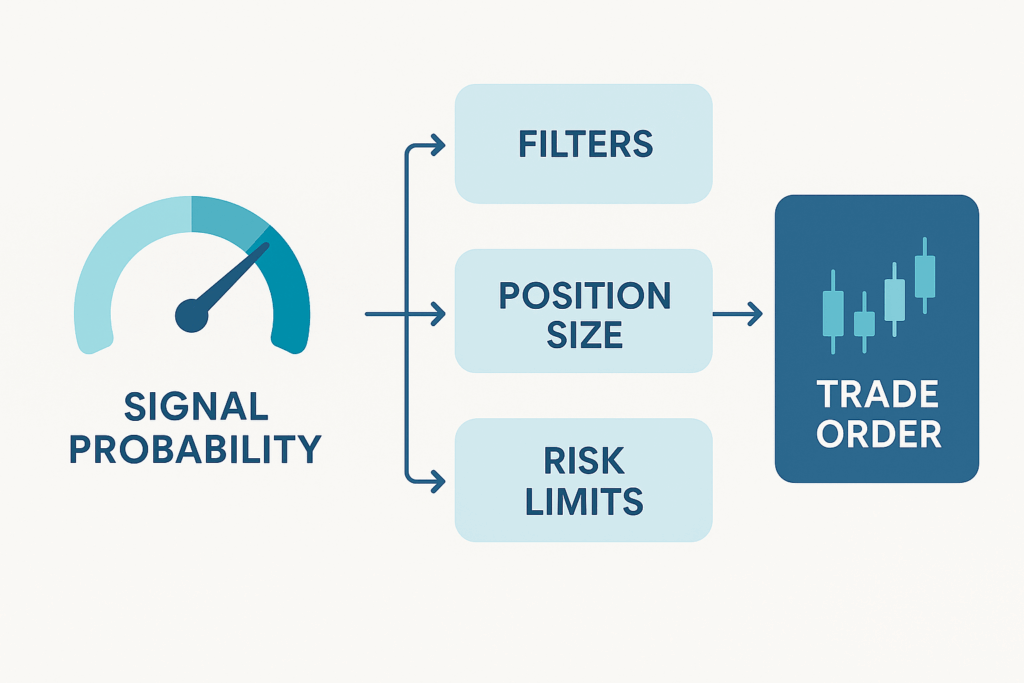
4. Decision Engine: Turning Probabilities into Real Trades
AI model outputs alone don’t make a bot. The real magic (and risk) lives in the decision layer that converts predictions into concrete trading actions.
4.1 Confidence Filters: When Not to Trade
Even a strong model will be wrong often. Good bots filter aggressively:
Example rules:
- Only go long if:
P(up) > 0.60and- regime classifier = “uptrend” and
- funding rate is not extreme (to avoid crowded long trades)
- Only go short if:
P(down) > 0.60- volatility is not already spiking (avoid shorting into a squeeze)
Everything else? No trade. Standing aside is a legitimate decision.
4.2 Position Sizing Logic
Next, the bot decides how much to risk.
A common approach:
- Base risk per trade = 1–2% of account
- Scale with model confidence:
- 60–65% → 0.5% risk
- 65–75% → 1% risk
- 75% → 1.5% risk (with tight controls)
Factor in volatility:
- Higher ATR / realized volatility → reduce size, widen stop
- Lower volatility → slightly larger size, tighter stop
Good bots embed position sizing and max exposure rules that are independent of how “excited” the AI model is.
4.3 Translating Signals into Entries & Exits
Even after a “buy” signal and a position size, robust bots still use technical and structural rules:
- Entry types:
- Market order (instant, but slippage)
- Limit order (better price, risk of no fill)
- Conditional order (only enter if price confirms a breakout)
- Stop-loss & take-profit logic:
- ATR-based stops (farther away in high volatility)
- Multiple take-profit levels (scale out at +3%, +5%, etc.)
- Time-based exit (close after X hours even if TP/SL not hit)
In many AI systems, the model doesn’t “know” about your exact stop or order type. It provides probabilistic guidance; the strategy layer decides how to express it in the market.
5. Execution Layer: How Orders Hit Binance, Bybit, or a DEX
Once the decision is made, the bot must actually execute the plan. This is where infrastructure matters.
5.1 CEX Execution Flow
On centralized exchanges (Binance, Bybit, OKX, etc.), the bot typically:
- Authenticates with API keys (stored encrypted)
- Checks balances and any open positions
- Sends order requests (REST or WebSocket):
- Side: buy/sell
- Quantity: e.g. 0.03 BTC
- Type: market / limit / stop
- Price (for limit) and other parameters
- Listens to order updates via WebSocket streams
- Handles partial fills, cancellations, and modifications
There are practical constraints:
- Latency: slow connections → more slippage
- Rate limits: exchanges cap API calls; spamming leads to bans
- Downtime: maintenance windows or sudden outages
Smart execution logic might include:
- Breaking large orders into smaller slices
- Avoiding illiquid pairs
- Cancelling and re-posting stale limit orders
5.2 DEX / On-Chain Execution
For on-chain strategies (Uniswap, GMX, Perp DEXs, Telegram bots):
- The bot constructs a transaction calling a smart contract function
- Signs the transaction with a private key (in a secure signer or wallet)
- Broadcasts to the network via an RPC provider
- Waits for confirmation and final state (e.g. position opened, liquidity added)
Extra on-chain challenges:
- Gas spikes during high volatility
- MEV attacks (sandwiching, frontrunning)
- Contract risk (vulnerable or malicious contracts)
This layer is one of the main reasons why on-chain “AI bots” are not beginner-friendly. The technical stack is more complex, and failure modes can be brutal.
6. Feedback & Learning: How AI Bots Adapt Over Time
A serious AI trading system isn’t static code you deploy once and forget. It’s an evolving system with a feedback loop.
6.1 Performance Tracking
The bot (or platform) continuously logs:
- Trade-by-trade PnL (gross & net after fees)
- Max drawdown and volatility of returns
- Win rate and average win vs average loss
- Performance by asset, timeframe, and market regime
These metrics are compared against benchmarks, for example:
- Buy-and-hold BTC
- A simple moving average strategy
- Risk-free yield (e.g. T-bills or stablecoin yields)
If an “AI strategy” can’t beat simple baselines after fees and risk, its complexity isn’t justified.
6.2 Model Retraining & Parameter Tuning
Over time, the bot developers may:
- Retrain models on more recent data
- Add or remove features that prove noisy or useless
- Adjust thresholds (e.g. only trade when confidence > 65% instead of 60%)
Done right:
- Retraining is infrequent (e.g. weekly/monthly),
- Changes are backtested and forward-tested before going live,
- Risk limits stay conservative while new logic is validated.
Done badly:
- Models are tweaked constantly based on short-term performance
- Strategies get overfit to recent noise
- Live performance degrades despite “constant optimization”
As a user, you want transparency on how often models change and how the platform validates updates.
7. What AI Bots Do Well – and Where Humans Still Matter
Understanding internals gives you a realistic view of strengths and limits.
7.1 Where AI Bots Are Strong
- Handling data overload: AI bots can process dozens of indicators, on-chain metrics, and sentiment feeds simultaneously.
- Consistency: once rules and models are set, execution is emotion-free and repeatable.
- Adaptation: regime detection and volatility-aware sizing can adjust faster than manual traders.
- Scale: one bot can manage multiple pairs and strategies in parallel.
7.2 What They Cannot Do
- Guarantee profit: predictions are probabilities, not certainties.
- See black swans coming: unexpected regulatory decisions, hacks, wars, or macro shocks still wreck models.
- Replace judgment: deciding which bot to run, how much capital to allocate, and when to pause is still a human responsibility.
- Remove market risk: you can reduce emotional and execution risk, but you still take directional or basis risk every time you enter a position.
The traders who succeed with AI bots treat them as tools inside a broader system, not as a replacement for thinking, risk management, or continuous learning.
8. Practical “Mechanics” Checklist for Evaluating AI Bots
In your Day 1 guide, you already cover security, general risk, scams, and high-level evaluation.
Here’s a mechanics-focused checklist you can use specifically for AI systems:
- Prediction Target
- What does the model predict? Direction? Returns? Regimes?
- On what timeframe (15m, 1h, 4h, daily)?
- Data Inputs
- Which inputs does the AI use: only price/volume, or also on-chain and sentiment?
- Are any inputs proprietary or third-party? What happens if those feeds break?
- Decision Rules
- How does the platform turn model outputs into position sizes and entries/exits?
- Are risk caps (max position, max leverage, daily loss limits) configurable by you?
- Execution Stack
- Which exchanges or chains are supported?
- Does the bot sit on their servers or yours?
- How do they handle latency, rate limits, and partial fills?
- Retraining & Updates
- How often is the AI retrained?
- How are new models validated before being deployed?
- Do they publish performance changes after major updates?
- Auditability
- Can you see why a trade happened (logs of signals, features, regimes)?
- Can you export trade history and run your own analysis?
If a platform can answer these clearly, that’s a good sign. If the answer to everything is “secret proprietary AI,” treat that as a warning.
Discover more from aiCryptoBrief.Com
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.



3 Comments
Pingback: 7 AI Trading Bot Mistakes & How to Avoid Them (2025) - aiCryptoBrief.Com
Pingback: How to Backtest and Paper Trade AI Crypto Bots (2025) - aiCryptoBrief.Com
Pingback: AI Crypto Brief – This Week’s Top Narratives, On-Chain Moves and Bot Setups - aiCryptoBrief.Com