Decentralized Finance—or DeFi—represents one of the most transformative innovations in global finance since the creation of modern banking. By leveraging blockchain technology and smart contracts, DeFi enables individuals to access financial services like lending, borrowing, trading, and earning yields without relying on banks, brokers, or other centralized intermediaries.
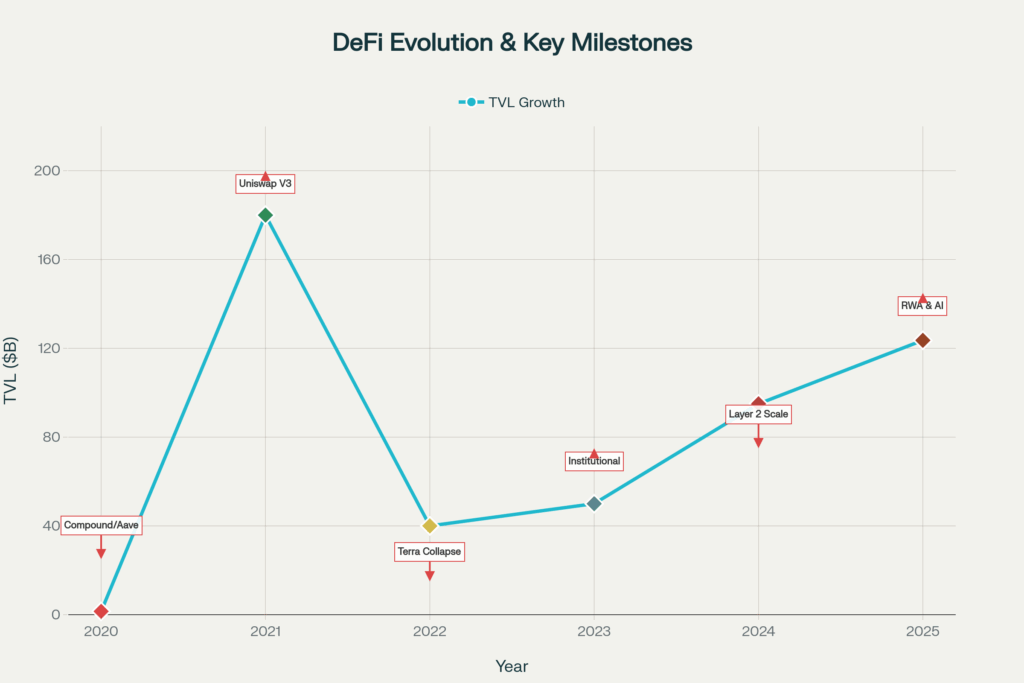
In 2025, DeFi has evolved from an experimental ecosystem into a robust alternative financial infrastructure. With Total Value Locked (TVL) reaching $123.6 billion globally and over 14.2 million unique wallets actively participating, DeFi is reshaping how people invest, save, and transact across borders. The beauty of DeFi lies in its promise: open access to finance for anyone with an internet connection, complete transparency through immutable blockchain records, and ownership of one’s own assets through non-custodial wallets.
This comprehensive guide explores what DeFi is, how it works, its key applications, the benefits and risks it presents, and the practical steps to engage with it safely. Whether you’re a beginner curious about decentralized finance or an intermediate user looking to deepen your knowledge, this article provides everything you need to understand this revolutionary financial system.
1. Understanding DeFi: The Basics
What is Decentralized Finance?
DeFi is a financial ecosystem built on blockchain networks—primarily Ethereum—that uses smart contracts to automate financial transactions and services without centralized intermediaries. Rather than trusting a bank to hold your money or a broker to execute your trades, you place trust in transparent, auditable code running on a decentralized network.
At its core, DeFi operates on three fundamental principles:
- Permissionless Access: Anyone with a wallet and internet connection can participate, regardless of location, credit history, or bank account status.
- Transparency: All transactions and smart contract logic are recorded on-chain and publicly verifiable, eliminating hidden fees or opaque operations.
- Ownership & Control: Users maintain complete control of their private keys and assets. No platform or institution can freeze funds, impose withdrawal limits, or restrict access.
The Technology Behind DeFi
DeFi is built on three essential technological pillars:
- Blockchain Technology: The foundation is a distributed ledger—typically Ethereum, but also Solana, Avalanche, BNB Chain, and others—that records all transactions transparently and immutably.
- Smart Contracts: These are self-executing programs stored on the blockchain. They automatically perform transactions when specific conditions are met, eliminating the need for human intermediaries. For example, a smart contract can automatically issue a loan when borrowers deposit collateral, or automatically liquidate positions if collateral values fall below thresholds.
- Token Standards: Tokens like ERC-20 (on Ethereum) and BEP-20 (on BNB Chain) are standardized ways of representing digital assets on blockchains, enabling seamless interaction between different DeFi protocols.
Dominant Blockchains in DeFi (2025)
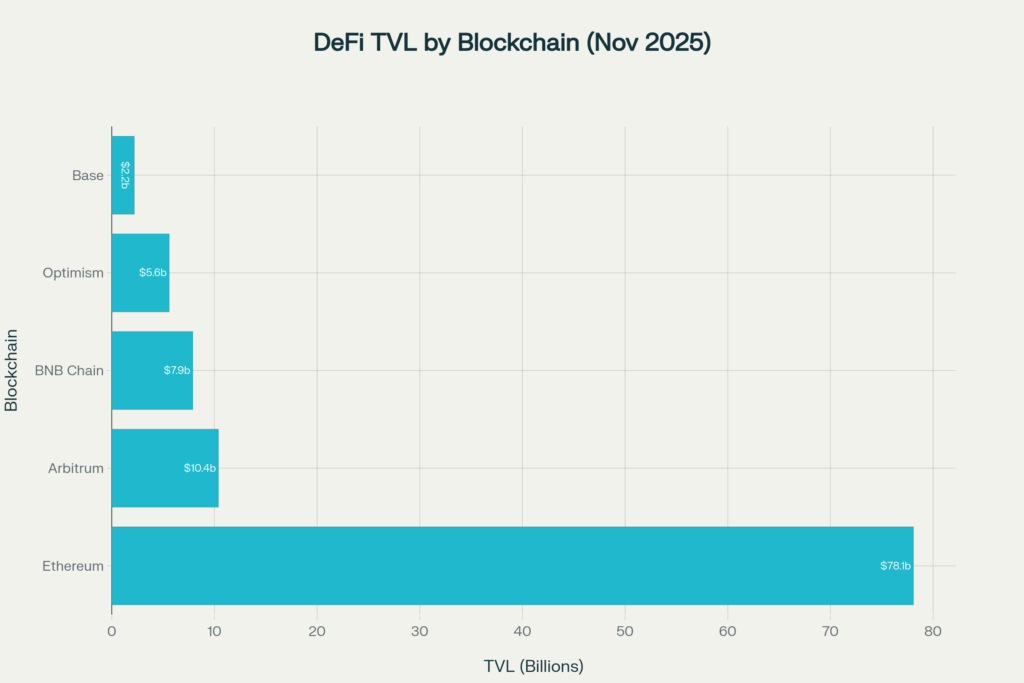
While Ethereum remains the backbone of DeFi with 63% of total TVL and $78.1 billion locked, the ecosystem has diversified across multiple chains:
- Ethereum: The original and most-used DeFi platform, hosting the majority of protocols and liquidity
- Solana: Rapid growth to 7.3% market share, offering high speed and low costs
- Arbitrum: Layer 2 solution with $10.4 billion TVL, showing 70% year-over-year growth
- Optimism: $5.6 billion TVL, more than doubling from 2024
- BNB Chain: $7.9 billion TVL, popular for Asian users
- Base (Coinbase Layer 2): $2.2 billion TVL, emerging as a growing hub
Pro Tip: Different chains offer different trade-offs. Ethereum offers maximum liquidity and security; Layer 2s like Arbitrum and Optimism offer lower fees; Solana excels at speed and cost efficiency. Choose based on your use case and risk tolerance.
2. DeFi vs Traditional Finance (CeFi)
Understanding how DeFi differs from traditional Centralized Finance (CeFi)—including banks, brokers, and centralized exchanges—is essential for appreciating why decentralization matters.
| Aspect | DeFi (Decentralized) | CeFi (Centralized) |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Users control private keys and assets | Institution controls funds and access |
| Access | Open 24/7 to anyone globally | Subject to business hours and regional restrictions |
| Fees | Often lower; protocol-determined | Higher fees; institution-set |
| Transparency | Fully auditable on-chain transactions | Limited transparency; trust-based |
| Custody | Non-custodial; self-sovereign | Custodial; third-party risk |
| Speed | Near-instantaneous (minutes) | Slower; subject to processing delays |
| Regulation | Evolving; less clear | Established frameworks; more oversight |
| Recourse | Limited if protocols fail | FDIC/regulatory protections exist |
| Accessibility | No credit checks or approval needed | Subject to credit scores, KYC requirements |
| Privacy | Pseudonymous transactions | Full identification required |
Key Differences Explained
- Permissionless vs Gatekept: Banks decide who can open an account. DeFi protocols don’t care who you are—if you have a wallet, you can participate.
- Transparency vs Trust: With DeFi, you can audit the smart contract code yourself. With banks, you trust their reputation and regulatory oversight.
- Composability: DeFi protocols are “money legos”—they connect seamlessly. You can use output from one protocol as input to another, creating complex financial strategies. Traditional finance is siloed.
- Global and Borderless: DeFi operates across all borders instantly. Traditional finance is bound by geographic and regulatory jurisdictions.
[Visual Suggestion: Side-by-side comparison infographic with icons for each aspect (lock for control, clock for access, money bag for fees, eye for transparency, etc.), showing DeFi on left, CeFi on right]
3. Core Components of DeFi
The DeFi ecosystem comprises several interconnected components. Understanding each one gives you a complete picture of how decentralized finance works.
3.1 Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs) and Automated Market Makers (AMMs)
What are DEXs?
Decentralized Exchanges allow users to trade crypto assets directly from their wallets without depositing funds into a centralized platform. Instead of traditional order books where buyers and sellers match, most DEXs use Automated Market Makers (AMMs)—a revolutionary innovation that enables permissionless trading.
How AMMs Work
AMMs operate through liquidity pools: smart contracts that hold reserves of two different tokens. When you want to trade, you swap directly against the pool, not against another person.
The mechanics are governed by a simple but powerful formula:
textx × y = k
Where:
- x = reserve of token A
- y = reserve of token B
- k = constant product (always remains the same after each trade)
Example: If a pool contains 1,000 ETH and 2,000,000 USDC, the constant k = 2,000,000,000,000. When you buy ETH by depositing USDC, the ratio shifts. To maintain the constant, the pool calculates the exact amount of ETH you receive.
Key AMM Advantages:
- Instant Liquidity: No waiting for order matches; liquidity is always available
- Low Barriers: Anyone can provide liquidity and earn fees
- 24/7 Trading: Markets never close; trade anytime
- Composability: Output can feed into other protocols
Popular DEXs (2025):
- Uniswap: The largest DEX with the most liquidity across thousands of token pairs
- Curve Finance: Specialized in stablecoin trading with extremely low slippage
- PancakeSwap: Popular on BNB Chain with high trading volume
- Jupiter: The leading aggregator on Solana, combining multiple liquidity sources
- Balancer: AMM with customizable pool weights and compositions
Liquidity Providers (LPs) and LP Tokens
When you provide liquidity to an AMM pool, you deposit equal values of both tokens. In return, you receive LP tokens representing your share of the pool. These LP tokens entitle you to:
- A proportional share of trading fees generated by the pool
- Your original tokens when you withdraw
Note: Providing liquidity carries impermanent loss risk—a temporary loss if the price ratio of your tokens changes significantly. This is explained in detail in the Risks section below.
3.2 Lending and Borrowing Protocols
How DeFi Lending Works
Lending protocols allow users to earn interest on their crypto holdings while enabling others to borrow against collateral. The process is entirely automated through smart contracts.
The Mechanism:
- Lenders deposit assets into a liquidity pool
- Smart contracts calculate interest rates algorithmically based on supply and demand
- Borrowers deposit collateral (typically 125-200% of the loan value)
- Loans are issued automatically when conditions are met
- Liquidations occur automatically if collateral value drops below the required threshold
Interest Rate Model
Most protocols use dynamic interest rates that adjust based on utilization ratio (percentage of pool funds loaned out). Higher utilization = higher interest rates to incentivize more deposits and borrowers to repay.
Top Lending Platforms:
Aave: The largest lending protocol with $40+ billion TVL, operating across 14+ blockchains. Features include:
- Flash loans (instant, uncollateralized borrowing for arbitrage)
- Variable and fixed interest rates
- Collateral swapping capabilities
- Governance through AAVE tokens
Compound: Pioneer of DeFi lending with algorithmic rate-setting. Known for:
- Simplicity and predictability
- cTokens (interest-bearing tokens representing your deposit)
- Conservative approach to asset listing
- Long track record of security
Morpho: Emerging as an alternative offering:
- Peer-to-peer lending matching
- Higher interest rates for both lenders and borrowers
- Lower fees than traditional protocols
Collateralization and Liquidation
In DeFi, loans are overcollateralized—you must deposit more collateral than you borrow. Why?
- Risk Management: Protects the protocol if asset prices fall
- No Credit Checks: Without credit history, collateral is the only recourse
- Automatic Enforcement: Smart contracts execute liquidations instantly
Example: You deposit 2 ETH (~$6,000) as collateral and borrow 3,000 USDC. If ETH price falls and your collateral drops below 3,750 USDC, liquidators can sell your ETH to repay the loan, typically incurring a liquidation penalty of 5-10%.
Warning: Liquidation risk is real, especially during market volatility. Always maintain a healthy collateral ratio (often 200%+ is safer).
3.3 Yield Farming and Staking
Yield Farming
Yield farming involves providing liquidity or lending assets to DeFi protocols in exchange for rewards, typically in the form of governance tokens or additional yield.
Example Strategy:
- Deposit $10,000 worth of ETH and USDC into Uniswap
- Receive $10,000 of LP tokens
- Earn 0.25% fees on every trade in that pool
- Earn additional UNI tokens as rewards (governance incentives)
- Total potential APY could be 5-20%+ depending on pool popularity
Risks of Yield Farming:
- Impermanent Loss: Price divergence between token pairs reduces LP returns
- Smart Contract Risk: Protocol vulnerabilities could lead to fund loss
- Rug Pulls: Scam projects disappear after attracting liquidity
- Volatility: High APY often reflects high risk
Staking
Staking involves locking tokens to secure a blockchain network and earn rewards. Unlike yield farming, staking doesn’t involve trading pairs.
Examples:
- Ethereum Staking: Lock ETH to validate transactions and earn 3-5% APY
- Lido (liquid staking): Stake ETH and receive stETH, which continues earning rewards while remaining liquid for use in DeFi
Liquid Staking Advantage: Traditional staking locks your assets. Liquid staking tokens (LSTs) like stETH, cbETH, and rETH allow you to earn staking rewards while still using your tokens in DeFi—a key trend in 2025.
3.4 Stablecoins and Synthetic Assets
Stablecoins: The Bridge Between Crypto and Traditional Finance
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a stable value, typically pegged to the U.S. dollar. They’re essential to DeFi because they eliminate volatility from many use cases.
Total stablecoin market capitalization exceeded $230 billion by mid-2025, representing roughly 7% of the total crypto market.
Types of Stablecoins:
Fiat-Backed (Centralized):
- USDT (Tether): Largest by market cap (~55% market share), issued by Tether with controversial reserve composition
- USDC (USD Coin): Transparent alternative issued by Circle, with monthly audits and conservative reserves
- PYUSD (PayPal USD): New entrant backed by PayPal and Paxos, targeting consumer and e-commerce use
- RLUSD (Ripple USD): Enterprise-focused stablecoin for cross-border payments
Decentralized/Algorithmic:
- DAI: The leading decentralized stablecoin backed by crypto collateral (primarily ETH and other assets), issued by MakerDAO with $5+ billion supply
- USDe (Ethena): Emerging protocol offering native staking yield
- FRAX: Hybrid protocol using a mix of collateral and algorithmic mechanisms
Synthetic Assets
Synthetic assets are blockchain-based tokens that represent the value of other assets without requiring direct ownership. For example:
- sUSD: Synthetic USD on Synthetix
- sBTC: Synthetic Bitcoin tracking BTC price
- sAAPL: Synthetic Apple stock (for crypto-native derivatives trading)
Synth assets enable traders to gain exposure to stocks, commodities, and forex without leaving the blockchain, creating a universal financial marketplace.
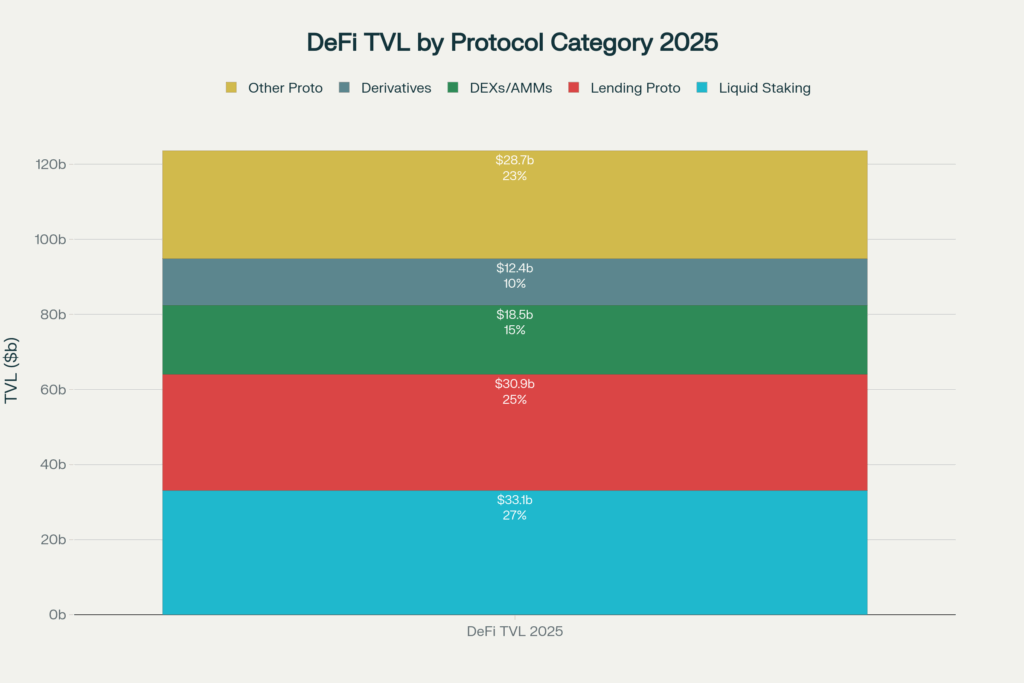
4. Benefits and Risks of DeFi
Benefits of Decentralized Finance
- Open Access: No gatekeepers. Anyone globally can access DeFi services with just a wallet and internet connection.
- Transparency: All transactions and smart contract code are public and auditable. No hidden fees or opaque operations.
- Lower Costs: By eliminating intermediaries, DeFi reduces fees. A loan on Aave typically costs 1-5% APY in interest, versus 6-10%+ at traditional banks.
- 24/7 Availability: Markets never close. Trade, lend, or stake anytime without business hour restrictions.
- Composability: DeFi protocols are modular and interconnected. You can build complex strategies by combining multiple protocols.
- Sovereignty: You own your private keys. No institution can freeze your funds, impose restrictions, or deny service.
- Yield Opportunities: DeFi offers significantly higher returns than traditional savings accounts (currently near 0%) through lending, staking, and yield farming.
Risks and Challenges of DeFi
Understanding risks is critical before participating. 2024 saw 69 major DeFi hacks costing over $735 million, emphasizing the need for caution.
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Smart contracts are code, and code can have bugs. High-profile examples:
- 2016 DAO Hack: $50 million lost due to a re-entrancy vulnerability
- 2021 Cream Finance: $130 million lost through protocol interaction exploits
- 2022 Ronin Network: $600 million stolen due to unaudited vulnerabilities
Even audited contracts aren’t guaranteed safe. Always check:
- ✅ Third-party security audits from reputable firms
- ✅ Bug bounty programs and responsible disclosure policies
- ✅ Time since launch and community scrutiny
- ✅ Code review by independent researchers
Impermanent Loss (IL)
When you provide liquidity to an AMM, you face impermanent loss—a temporary loss compared to simply holding the tokens separately.
Example: You deposit 1 ETH + 2,000 USDC into a pool. If ETH price doubles to $4,000, the AMM’s math forces you to hold more USDC and less ETH than if you’d just held both. If you withdraw before the price reverts, this becomes a permanent loss.
IL is higher in pools with volatile assets. Stablecoin pools (USDC/DAI) have minimal IL, while volatile pairs can experience 10-50%+ IL during market swings.
Liquidation Risk
Borrowers face liquidation if collateral value falls below thresholds. During market crashes, liquidations cascade, creating contagion effects across protocols.
Example: During a 20% market crash, many overleveraged borrowers simultaneously liquidate, flooding markets with collateral selling pressure—worsening the crash.
Regulatory Uncertainty
DeFi operates in an evolving regulatory landscape. Sudden changes could:
- Force protocol shutdowns
- Restrict access for certain jurisdictions
- Impose compliance costs that centralize protocols
- Create legal liability for users
Scams and Rug Pulls
With low barriers to entry, scammers create fake protocols promising unrealistic yields. Red flags include:
- 🚩 Promises of 1,000%+ APY
- 🚩 Anonymous team with no track record
- 🚩 No external audits
- 🚩 Concentrated governance power
- 🚩 Funds can’t be withdrawn easily
Front-Running and MEV (Maximal Extractable Value)
Miners and validators can reorder transactions to extract profits—a practice called MEV. In 2024-2025, MEV extraction on Ethereum totaled approximately $1.1-1.26 billion, directly reducing user returns.
MEV attacks include:
- Front-Running: Seeing your pending transaction and executing ahead of you to capture profit
- Sandwich Attacks: Executing trades before and after your transaction, capturing the price slippage you create
- Liquidation Extraction: Bots identifying liquidatable positions and frontrunning other liquidators
Defenses include:
- Using MEV-protection services (MEV-Boost, MEV blocklists)
- Trading on privacy pools or encrypted mempools
- Using aggregators that minimize slippage
Volatility Risk
Crypto assets are highly volatile. A 20-50% price swings in days are common. This affects:
- Collateral values (triggering liquidations)
- LP impermanent loss (expanding dramatically)
- Yield sustainability (protocols become insolvent under stress)
Systemic Risk
DeFi protocols are interconnected. A collapse in one can cascade to others. The 2022 Terra-Luna collapse demonstrated how contagion can spread rapidly, wiping out billions in collateral and exposing systemic fragility.
5. How to Start Using DeFi Safely: A Step-by-Step Guide
DeFi can seem intimidating, but following these steps will help you participate safely and with confidence.
Step 1: Set Up a Wallet
A crypto wallet is your gateway to DeFi. Choose one based on your needs:
Non-Custodial (Recommended for DeFi):
- MetaMask: Browser extension, most popular, easy for beginners
- Trust Wallet: Mobile-first, supports hundreds of chains
- Ledger/Trezor: Hardware wallets offering maximum security for long-term holdings
- Argent: Smart wallet with built-in security features and approval management
Why Non-Custodial?: You control your private keys. No platform can freeze or restrict your access.
Pro Tip: Use a hardware wallet (Ledger, Trezor) for storing significant amounts. Hardware wallets keep private keys offline, protecting against online hacks.
Security Best Practice: Never share your seed phrase (recovery words). Anyone with this phrase can access all your funds.
Step 2: Fund Your Wallet
Transfer crypto from a centralized exchange (Coinbase, Kraken, Binance) to your wallet.
Recommended starting assets:
- Stablecoins (USDC, DAI): Start here for low-risk familiarization
- Ethereum (ETH): For paying gas fees and participation
- Small amounts: Never move large sums until you’re confident
Step 3: Connect to a DeFi Protocol
- Visit a DeFi platform (e.g., Uniswap, Aave, Curve)
- Click “Connect Wallet”
- Approve the connection in your wallet
- Start interacting
Always verify URLs before connecting. Phishing sites are common. Bookmark official URLs.
Step 4: Start Small
Recommended First Steps:
Option 1 – Stablecoin Lending (Lowest Risk)
- Deposit USDC to Aave
- Earn 3-5% APY with minimal risk
- Withdraw anytime
Option 2 – Stablecoin Liquidity Providing
- Deposit USDC + DAI to Curve
- Earn fees from stablecoin trades (~3-10% APY)
- Lower impermanent loss risk
Option 3 – Ethereum Staking
- Stake ETH or receive stETH (Lido’s liquid staking token)
- Earn 3-5% rewards
- Retain liquidity with stETH
Step 5: Apply Security Best Practices
Essential DeFi Security Checklist:
✅ Use unique, strong passwords for every platform
✅ Enable 2FA on all accounts
✅ Store recovery phrases offline (paper, metal backup, safe)
✅ Test transactions with small amounts first
✅ Regularly audit approvals using Revoke.cash—revoke unused app permissions
✅ Review smart contracts before use—use resources like DefiSafety.com
✅ Use transaction simulation to verify you’re approving the right action
✅ Diversify chains and wallets—don’t keep all funds in one place
✅ Avoid clicking links in Discord or Telegram—always navigate directly
✅ Keep software updated—browser, extensions, OS patches
Multi-Signature Wallets for Large Amounts: For substantial holdings, consider multisig wallets (Gnosis Safe, Ledger Multisig) requiring 2-of-3 approvals for transactions. Reduces single-key compromise risk by 60%+ compared to single-signature wallets.
Step 6: Understand Your Risks
Before depositing significant funds:
- Read the protocol’s documentation
- Check audit reports
- Review TVL and transaction history
- Understand liquidation risks if borrowing
- Know that smart contracts can fail; assume 0% recourse
6. The Future of DeFi in 2025 and Beyond
The DeFi landscape is rapidly evolving. Several key trends will shape the ecosystem’s next chapter.
6.1 Layer 2 Scaling and Cost Reduction
Current State: Ethereum mainnet gas fees ($5-20+ per transaction) remain a barrier for retail users. Layer 2 solutions are solving this.
Arbitrum and Optimism are leading the charge:
- Arbitrum: $10.4 billion TVL, 70% year-over-year growth
- Optimism: $5.6 billion TVL, more than doubled in 2025
- Base (Coinbase’s L2): $2.2 billion TVL, rapidly gaining adoption
Impact: L2s reduce transaction costs by 100x (from $10 to $0.10), enabling smaller trades and micropayments. Ethereum’s March 2024 Dencun upgrade further reduced L2 fees through blob-based data availability.
Future: Cross-chain unified liquidity through solutions like Stargate (LayerZero), Synapse, and Symbiosis will create a seamless multi-chain experience.
6.2 Real-World Assets (RWAs) Integration
RWAs represent the biggest bridge between traditional finance and DeFi. By 2025:
- RWA market cap reached $5+ billion
- Major institutions (BlackRock, Franklin Templeton, JPMorgan) launched tokenized products
- MakerDAO uses RWA collateral for DAI stability
RWA Examples:
- Tokenized US Treasury Bonds: Earn Treasury yields on-chain
- Real Estate Tokenization: Fractional ownership of properties
- Trade Finance: Tokenized letters of credit and invoices
- Commodity Exposure: Gold, oil, and other commodities as on-chain assets
Impact: Trillions in traditional assets could flow on-chain over the next decade, dwarfing today’s DeFi TVL.
6.3 AI and Automation in DeFi (DeFAI)
Artificial intelligence is fundamentally changing how DeFi operates:
Smart Automation:
- AI handles real-time liquidity rebalancing
- Dynamic interest rate adjustments based on market conditions
- Predictive models for liquidation management
- Automated arbitrage execution
Personalization:
- AI suggests optimal yield strategies based on your wallet
- Auto-switches farming positions to capture best returns
- Recommends collateral adjustments before liquidation risk
Efficiency:
- Reduces human error and manual monitoring
- Enables capital efficiency improvements
- Allows protocols to adapt to volatile markets automatically
Leading Projects: Zeebu, Morpho, and other emerging protocols are integrating AI for superior capital allocation.
6.4 MEV Solutions and Privacy
2025 marks a turning point in MEV mitigation:
Current Solutions:
- MEV-Boost: Separates block proposers from builders, increasing staking rewards by up to 60%
- Private Mempools: Hide pending transactions, reducing front-running
- Encryption Layers: Encrypt transaction data until execution
Emerging Solutions:
- Threshold encryption: Decrypt transactions only after ordering (prevents front-running entirely)
- Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs): Process transactions in secure enclaves
- Encrypted mempools on more chains: Currently available on Ethereum, expanding to L2s
Impact: Institutional adoption requires protection from MEV. These solutions will make DeFi accessible to traditional finance participants.
6.5 Cross-Chain Interoperability
DeFi is no longer single-chain. Protocols like Stargate, Synapse, and 1inch enable seamless asset transfers across 30+ blockchains.
Benefits:
- Unified liquidity pools across chains
- Reduced user friction (no manual bridging)
- dApps access users on all chains simultaneously
- Emerging L1s and L2s now tap into mega-liquidity
Trend: By 2026, users will perceive “DeFi” as one unified ecosystem, not fragmented chains.
6.6 Institutional Participation and Regulatory Clarity
2025 represents the beginning of institutional integration:
Catalysts:
- Clear regulatory frameworks (MiCA in Europe, potential GENIUS Act in US)
- Stablecoin clarity enabling enterprise payments
- Custody solutions and insurance products
- RWA tokenization attracting traditional asset managers
Impact: Institutional capital inflows could push DeFi TVL to $500 billion+ by 2027.
7. Frequently Asked Questions About DeFi
What is a DeFi Token?
DeFi tokens are cryptocurrencies issued by decentralized protocols, typically serving two purposes:
Governance: Token holders vote on protocol changes (fee structures, risk parameters, new features)
Utility: Some tokens are staked for yield, used as collateral, or provide access to protocol features
Examples:
- UNI (Uniswap): Governance token; holders vote on fee distribution and new features
- AAVE (Aave): Governance and collateral option; holders earn protocol revenue
- COMP (Compound): Governance token for community decision-making
- CRV (Curve): Incentivizes liquidity provision and governance
Is DeFi Safe?
Short answer: DeFi is as safe as the individual protocol and your own security practices.
Factors affecting safety:
- ✅ Audited smart contracts (multiple audits = safer)
- ✅ Established track record (launched 3+ years ago without major hacks)
- ✅ Significant TVL (larger TVL = more scrutiny and decentralization)
- ✅ Your security practices (hardware wallet, not using phishing links, auditing approvals)
Not safe:
- ❌ New protocols with no audit history
- ❌ Promises of unrealistic yields (1000%+ APY)
- ❌ Anonymous teams
- ❌ Centralized governance (one person controls protocol changes)
Reality Check: Aave and Compound have operated for 5+ years without major security incidents and hold 40%+ of all DeFi TVL. They’re the “blue chips” of DeFi.
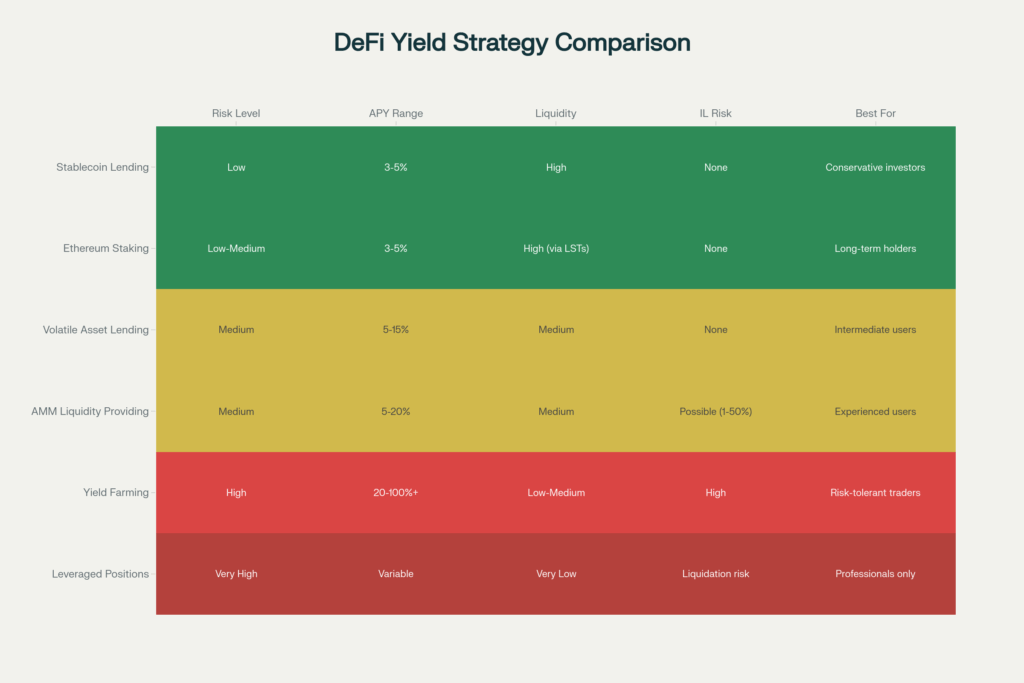
How Can I Earn Yield in DeFi?
Multiple yield strategies exist, each with different risk-return profiles:
Low Risk (~3-5% APY):
- Stablecoin lending (USDC to Aave)
- Ethereum staking (via Lido)
- Stablecoin LPing (Curve pools)
Medium Risk (~5-15% APY):
- Volatile token lending (ETH to Aave)
- Volatile LP provision (ETH/USDC on Uniswap)
- Liquid staking derivatives (stETH farming)
High Risk (15%+):
- Yield farming incentive programs
- New protocol airdrops
- Complex derivative positions
Pro Tip: APY claims of 100%+ typically indicate either (1) temporary incentive programs that will reduce, (2) high-risk protocols with significant liquidation danger, or (3) scams.
What are Gas Fees?
Gas fees are payments for blockchain transactions. They compensate miners/validators for processing transactions.
Ethereum mainnet: $5-20+ per transaction (higher during congestion)
Layer 2s: $0.10-1 typically
Solana: $0.00025 per transaction
Gas is paid in the chain’s native token (ETH for Ethereum, SOL for Solana).
Cost implications:
- Small trades ($100) on Ethereum can cost $10+ in gas (~10% fee)
- Same trade on L2 costs $0.50 (0.5% fee)
- Same trade on Solana costs $0.001 (negligible)
Optimization: Always check gas prices before transacting. Use Layer 2s for frequent small trades; mainnet for large transactions where gas is a smaller percentage of value.
Will DeFi Replace Traditional Banks?
Realistic Answer: Not in the next 5-10 years, but DeFi will coexist with banking.
Why DeFi won’t fully replace banks:
- Users still want regulatory protection and insurance
- Custody complexity deters many retail users
- Fiat on-ramps remain limited
- Emerging market adoption requires stable institutions
Likely Future:
- Banks will integrate DeFi rails and blockchain technology
- Hybrid models combining CeFi and DeFi will emerge
- DeFi captures 20-30% of financial services by 2030
- Traditional finance adopts blockchain infrastructure, reducing the “DeFi vs Banking” distinction
Practical Today: DeFi is best for users who want sovereignty, transparency, and yield. Traditional banks remain better for basic checking accounts, mortgage lending, and regulatory protection.
8. Final Thoughts
Decentralized Finance represents a fundamental reimagining of how humans access and manage money. By leveraging blockchain technology and smart contracts, DeFi removes barriers, reduces costs, and offers unprecedented financial autonomy to anyone with an internet connection.
In 2025, DeFi has matured from an experimental ecosystem into a robust infrastructure capable of supporting billions in digital assets. With over $123 billion in TVL, Aave and Compound serving millions of users, and institutional adoption accelerating, DeFi is no longer niche—it’s foundational to the future of finance.
However, DeFi is not risk-free. Smart contract vulnerabilities, market volatility, and regulatory uncertainty remain real threats. Success in DeFi requires continuous learning, cautious risk management, and commitment to security best practices.
If you’re ready to explore decentralized finance:
- Start with low-risk strategies (stablecoin lending or Curve pools)
- Use established protocols (Aave, Uniswap, Curve, Lido)
- Never risk more than you can afford to lose
- Audit approvals and monitor your positions regularly
- Stay informed—DeFi evolves rapidly
The next chapter of finance is being written on blockchains, executed through smart contracts, and governed by communities worldwide. DeFi invites you to participate not just as a user, but as an owner, stakeholder, and architect of this transformation.
Next Steps
Ready to dive deeper into DeFi?
🔗 Explore the companion article: “Top 10 DeFi Platforms in 2025 – Best Tools for Trading, Lending, and Earning Yield” — a detailed breakdown of the most trusted platforms, their features, and ideal use cases.
Discover more from aiCryptoBrief.Com
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.


4 Comments
Pingback: Stablecoins Explained: The Bridge Between Traditional Currency and Crypto (2025) - aiCryptoBrief.Com
Pingback: How to Earn Passive Income with Yield Farming (2025 Guide) - aiCryptoBrief.Com
Pingback: What is DeFAI? The Complete Guide to Artificial Intelligence in Decentralized Finance (2025) - aiCryptoBrief.Com
Pingback: Top 5 DeFi Applications You Should Try Today (2025 Guide) - aiCryptoBrief.Com